The impact of temperature on archives
(1) The mechanism of temperature acting on archives
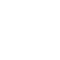
Temperature mainly affects the materials used in archive production through the following two pathways.
① Promoting the phase transition of macromolecules in archival materials. Archival materials are composed of large molecules composed of many atoms and atomic groups, which are constantly in vibration. The vibration frequency is closely related to the ambient temperature. As the ambient temperature increases, the vibration frequency of macromolecules increases and the amplitude becomes stronger. When the temperature rises to a specific level, archival materials can undergo separation and depolymerization of side functional groups, as well as main chain cleavage. As a result, due to changes in the structure of macromolecular substances, their properties also undergo corresponding changes.
② Changing the activation energy of chemical reactions can lead to various reactions such as oxidation, hydrolysis, and peeling of the main components of paper. The occurrence and degree of various reactions depend on the activation energy of the substances participating in the reaction. Activation energy refers to the difference in average energy between activated state molecules and reactant state molecules, and is a temperature dependent quantity. As the temperature increases, the number of activated molecules increases, leading to an increase in the number of effective collisions and an accelerated reaction rate. From the principle of chemical reactions, it can be inferred that temperature is an important factor affecting the rate of chemical reactions. For general chemical reactions, the higher the temperature, the faster the chemical reaction rate; The lower the temperature, the slower the chemical reaction rate.
(2) The effect of temperature on the performance of archives
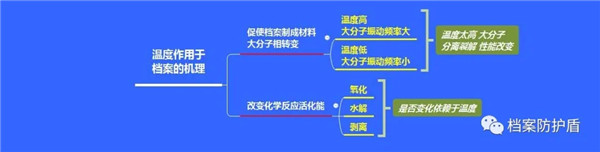
Temperature can not only affect paper archives, but also have an impact on new types of archives such as film archives, magnetic carriers, and optical discs. Experiments have shown that under the condition of relative humidity of 65%, increasing the storage condition of paper from 15 ℃ to 25 ℃ results in an average reduction of 2.8% in tear strength, 13.1% in folding strength, 5.5% in tensile strength, and 2.8% in burst strength. High temperatures accelerate the destructive effects of various harmful chemicals and organisms on archival paper.
High temperature causes oil diffusion in handwriting materials with poor heat resistance. The melting point of oil and wax, which serve as color solvents, is generally not high. When handwriting is stored at high temperatures for a long time, oil leakage may occur, and the handwriting gradually spreads. In severe cases, the handwriting is blurry and cannot be read. High temperatures can promote the damage of oxygen and other harmful gases to silver images, causing micro spots.
Low temperature is usually beneficial for the durability of archives, but this does not mean that the lower the temperature in the warehouse, the better. If the temperature is too low, the water in the archival materials is prone to freezing, and the internal structure is damaged, which is not conducive to its durability.
(1) The mechanism of humidity on archives
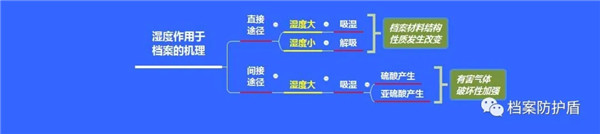
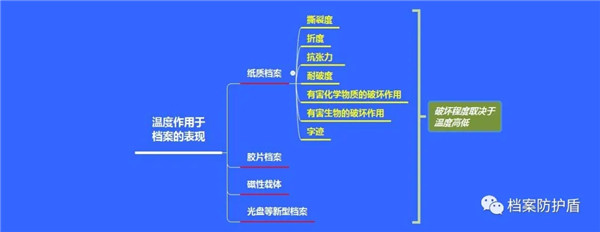
① The materials produced through direct access to archives exhibit hygroscopicity and desorption in different humidity environments. At specific temperatures and high environmental humidity, the moisture content of archival materials increases, resulting in moisture absorption. When moisture absorbing archives are transferred to medium to low humidity environments, the moisture content of the materials used in the archives will decrease, resulting in desorption. In this way, changes in humidity directly cause changes in the structure of the materials used in archive production, inevitably leading to changes in their properties.
② Indirect pathways: With the increase of environmental humidity, the hygroscopicity of archives increases, and harmful gases in the environment (especially acidic gases) have an enhanced destructive effect on the materials used for archival production. Taking sulfur dioxide as an example, it can dissolve in water to form sulfite, which, under the action of a catalyst, further reacts with oxygen in the air to form sulfuric acid. These two acidic substances can dissociate hydrogen ions, providing conditions for the acidic hydrolysis of archival materials, which is particularly evident in paper archives.
(2) The Effect of Humidity on Archives
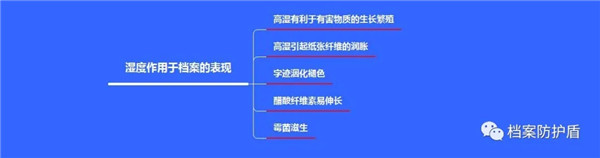
High humidity increases the moisture content of paper, and harmful substances in the air can directly or indirectly cause chemical reactions in cellulose, leading to damage to the paper archive carrier. High humidity is conducive to the growth and reproduction of harmful organisms. When the environmental humidity is high, the moisture content of the materials used to make archives increases, and harmful organisms obtain more moisture through harmful archives, which is more beneficial for their growth and reproduction and causes greater damage to the archives. On the contrary, it is unfavorable for its growth and reproduction, and has less damage to the archives. High humidity causes the swelling of paper fibers, which enhances their moisture absorption and reduces their tensile strength. If the relative humidity changes frequently, it can cause repeated expansion and contraction of the paper, causing damage to the paper fibers. Placing archives in a high humidity environment for a long time can easily lead to them becoming "bricks". Experiments have shown that as environmental humidity increases, the mechanical strength of paper decreases sharply.
High humidity causes handwriting materials with poor water resistance to liquefy and fade. At the same time, in humid conditions, oxidizing gases from the air can react with water to generate primitive oxygen: this primitive oxygen has a bleaching effect and can promote the bleaching and fading of handwriting. Some researchers have pointed out that under the same temperature and load conditions, the elongation of cellulose oxalate increases with the increase of relative humidity.
In addition, mold is easy to breed in high humidity environments, which can damage both paper and gelatin emulsion layers. When the environmental humidity is too low, the moisture contained in the archival materials evaporates outward, which cannot maintain their normal moisture content. This causes the archival materials to become hard and brittle, with reduced flexibility and strength, just like plastic loses its plasticizer and becomes brittle and hard. In the northwest region of China, archives are exposed to low humidity and dry environments for a long time, which can easily become brittle and reduce their durability.
Jiangxi Ruidun Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. has strong technical strength, adopts advanced CNC equipment, and focuses on new product research and innovation. Its main products include smart archive system equipment, smart library system equipment, smart campus system equipment, warehouse environment system equipment, smart dense shelves, smart bookshelves, smart shelves, and computer software and hardware product research and development. The company provides integrated solutions for smart archives. The product is reasonably priced and shipped quickly.
Contact number: 0795-7359222
Sales Department Contact Person: Yang Wei Phone: 18000759058





 赣公网安备 36098202000185号
赣公网安备 36098202000185号